Data analytics refers to qualitative and quantitative techniques and processes used to enhance productivity and business gain. Data is extracted and categorized to identify and analyse behavioural data and patterns, and techniques vary according to organizational requirements.
Data analytics is primarily conducted in business-to-consumer (B2C) applications. Global organizations collect and analyse data associated with customers, business processes, market economics or practical experience. Data is categorized, stored and analysed to study purchasing trends and patterns.
Evolving data facilitates thorough decision-making. For example, a social networking website collects data related to user preferences and community interests and segment according to specified criteria, such as demographics, age or gender. Proper analysis reveals key user and customer trends and facilitates the social network's alignment of content, layout and overall strategy.
Test Yantra provides testing services for Data Analytics, to its customers in the B2C segment
Big Data testing
Problem Statement:
- Test Data Management: Separation of required data from junk i.e. as the data ages it becomes obsolete, and needs to be dealt by removing it. Such voluminous data to needs to be audited to ensure that the data fit for business purposes.
- Building and understanding the test data: Selecting test data that represents the data that is used every day when the system is up. Not planning the logistics to store the huge volume of test data created to avoid problems.
- Business Rules understanding: Lack of understanding towards the data and the context of different data ‘states’ mapping to business flows. Lack of understand towards the business rules and the statistical correlation between different subsets of data.
- Understanding Big Data ecosystem: Lack of BD ecosystem understanding and ability to think beyond the regular parameters of automated testing. Lack of required skill-set inevitably and to leverage Big Data technologies.
- Test Data Automation: Lack of automation approach in order to create criteria and automate test data selection or creation process
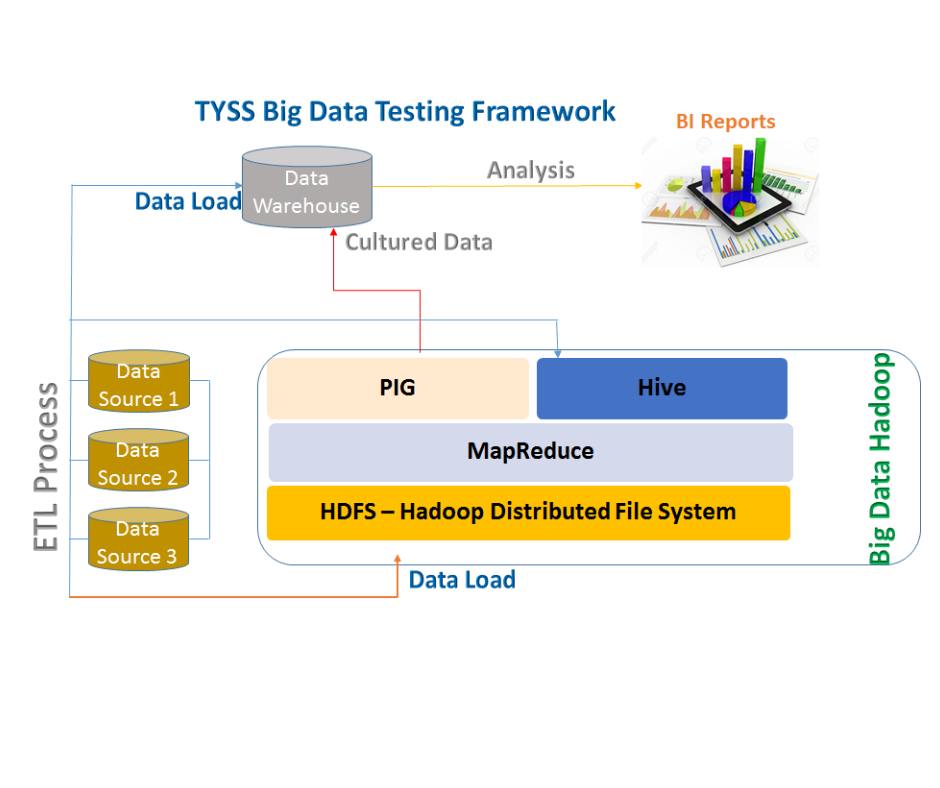
TYSS Big Data Testing Framework:
Cyber Security:
Problem Statement:
The most significant transformation in cyberspace is the emergence of a new form of conflict termed as cyber conflict in military affair/war, which is a blend of computer network attack and special technical operations, gradually becoming an imperative “act of war”.
Most Commonly executed Cyber-Attacks:
- Malware: It is a variety of cyber threats including Trojans, viruses, and worms which can be introduced to a system through software downloads, operating system vulnerabilities, email attachments etc.
- Phishing: Attacks are sent via email which may include a link that will guide the user to a dummy site designed to steal a user’s information and personal data.
- SQL Injection: It works by exploiting known SQL vulnerabilities that allow the SQL server to run malicious code to access user information.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): One of the most common ways an attacker can deploy a cross-site scripting attack is by injecting malicious code into a comment or a script that could run automatically and significantly damage the website by placing the users’ information at risk.
- Session Hijacking and Man-in-the-Middle Attack: An attacker can hijack the session by capturing the session ID, allowing them to log in as an unsuspicious user and gain access to the information on the web server.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS): Disrupting the service to a network, attackers send high volumes of data or traffic through the network until it becomes overloaded and stops functioning.
Few Common Security Testing Techniques:
Following is a list of a few critical security testing techniques that must be implemented in organizations to safeguard critical data and information:
- Penetration Testing: It simulates an attack from a malicious hacker, involves analysis of a system to check for potential vulnerabilities to an external hacking attempt.
- Vulnerability Scanning: It is done through automated software to scan a system to identify the weakness.
- Ethical Hacking: It’s hacking an organization’s software/systems with the intent to expose security flaws in the system.
- Risk Assessment: It involves analysis of security risks identified in an organization, classified as high, Medium and low. This assessment recommends controls, measures to reduce the risk.
- Security Auditing: An internal inspection of applications and operating systems for security flaws. Audit can also be done by inspection of code.
